Sign up for workout ideas, training advice, reviews of the latest gear and more.





Staying fit doesn’t have to mean spending every day in the gym. For women with busy schedules, a 2-day full body compound workout routine can deliver impressive results—boosting strength, improving endurance, and sculpting a toned physique in minimal time. This efficient training strategy focuses on compound movements, which work multiple muscle groups at once, helping you get the most out of each session.
In this article, we’ll break down everything you need to know about a 2-day full body compound workout routine: its benefits, structure, exercises, and progression tips. Whether you train at home or in the gym, this guide will help you maximize results while maintaining balance and recovery.
A 2-day full-body routine is perfect for women who want to build strength, burn calories, and stay consistent without overtraining. It’s also great for beginners, busy professionals, or those supplementing other activities like yoga, cycling, or Pilates.
You train your entire body in just two sessions per week. By using compound movements—like squats, rows, and presses—you target multiple muscle groups simultaneously, saving time while ensuring no major muscle is left out.
Compound exercises mimic natural movement patterns. They help you move better in daily life—lifting groceries, climbing stairs, or carrying kids—by strengthening multiple joints and muscles at once.
Because compound exercises engage large muscle groups, they elevate your heart rate and increase post-workout calorie burn through EPOC (Excess Post-Exercise Oxygen Consumption)—a key factor in long-term fat loss.
A 2-day full body plan provides enough stimulus for muscle growth without overwhelming your recovery capacity. It’s easy to stick to, prevents burnout, and offers measurable progress quickly.
Compound exercises engage two or more joints and multiple muscles at once. Examples include squats, deadlifts, bench presses, and pull-ups. Compared to isolation exercises like bicep curls or leg extensions, compound lifts are more efficient and functional.
When you perform a compound lift, your body recruits several muscle groups. For example:
This means you build total-body coordination, not just isolated muscle strength.
Compound movements trigger the release of anabolic hormones like testosterone and growth hormone—natural chemicals that promote muscle growth and fat loss. Women benefit from these hormones too, though in smaller amounts, leading to a leaner, more defined physique.
Because your body works harder during multi-joint lifts, your energy expenditure rises, creating a higher calorie burn during and after your workout.
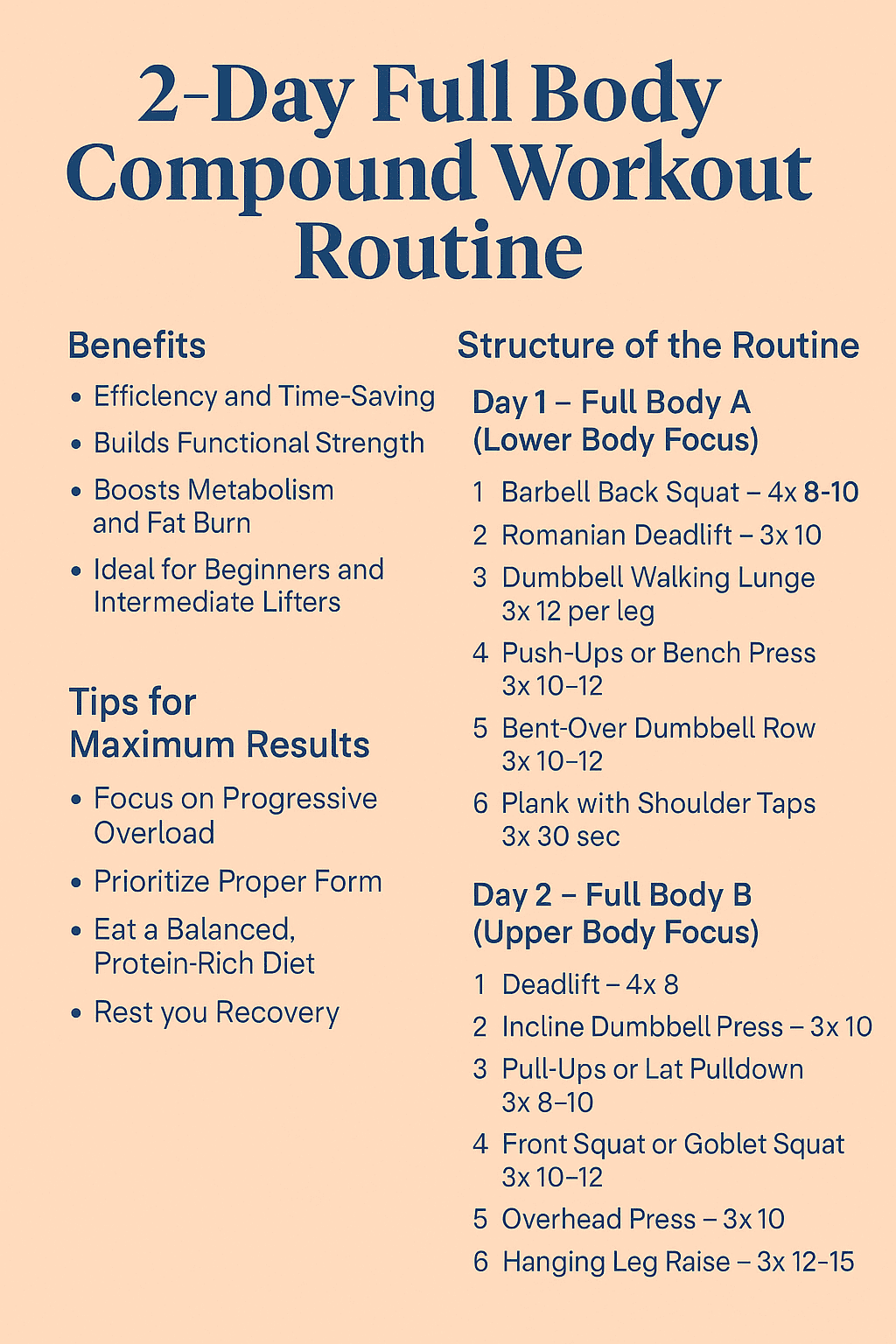
This program is split into two main sessions: Day 1 (Lower Body Emphasis) and Day 2 (Upper Body Emphasis). Both days still work your entire body, but each has a focus to balance strength development.
You’ll perform 4–6 compound exercises per session, training major movement patterns: push, pull, squat, hinge, and carry.
Allow 2–3 rest days between workouts for recovery and adaptation. For example:
or
This session emphasizes lower body strength and core stability, while still including upper-body compound lifts for balance.
One of the most effective compound lifts, squats build your legs and glutes while engaging your core.
Form Tip: Keep your chest up, core tight, and drive through your heels.
Targets your hamstrings, glutes, and lower back.
Form Tip: Maintain a flat back and hinge at your hips rather than your waist.
Lunges enhance balance, coordination, and unilateral leg strength.
Form Tip: Step forward with control, keeping your front knee aligned with your ankle.
A compound upper body exercise for chest, shoulders, and triceps.
Modification: Perform incline push-ups if you’re a beginner.
Works your upper back, rear shoulders, and core.
Form Tip: Keep your torso parallel to the floor and pull dumbbells toward your waist.
A dynamic core stabilizer that engages shoulders and abs.
Form Tip: Minimize hip sway and keep your core tight throughout.
This session focuses on pushing, pulling, and pressing movements for upper-body strength while incorporating lower-body compound moves for balance.
A total-body powerhouse that strengthens your posterior chain.
Form Tip: Engage your lats, keep the bar close to your body, and push through your heels.
Targets the upper chest, shoulders, and triceps.
Form Tip: Keep a slight arch in your back and avoid locking out elbows.
Enhances back width and grip strength.
Modification: Use assisted pull-ups or resistance bands if needed.
Focuses on quads and core engagement.
Form Tip: Keep your elbows high and chest upright.
Develops shoulder and triceps strength while improving posture.
Form Tip: Maintain a tight core to avoid arching your lower back.
Strengthens your lower abs and hip flexors.
Modification: Try lying leg raises if hanging variation is too challenging.
This increases blood flow, primes muscles, and reduces injury risk.
Stretching aids muscle recovery and improves flexibility.
Gradually increase your weights, reps, or sets every few weeks to keep challenging your muscles. This drives strength gains and muscle tone.
Never sacrifice technique for heavier weights. Good form ensures muscle activation, reduces injury risk, and leads to better long-term progress.
Support your workouts with nutrient-dense meals. Aim for lean proteins, complex carbs, and healthy fats. Protein helps repair muscles and fuels recovery.
Allow adequate rest between sessions. Remember, muscle growth happens during recovery—not during the workout itself.
Record your lifts and reps in a journal or app. Tracking builds motivation and ensures consistent improvement.
This 2-day compound workout routine is ideal for:
You can perform it at home with dumbbells, kettlebells, or a barbell—or at the gym with standard equipment.
If you enjoy additional activity, include 1–2 short cardio or mobility sessions:
These additions enhance endurance and support your strength training routine.
Use light weights and focus on correct technique.
Goal: Master each compound movement.
Add moderate weights and reduce rest time (60–90 seconds).
Goal: Build endurance and control.
Lift heavier (70–80% of your 1RM).
Goal: Boost muscle tone and overall strength.
After six weeks, take a deload week or switch to a different plan (e.g., a 3-day split or HIIT circuit).
Every session hits major muscle groups—legs, glutes, back, shoulders, and arms—for a well-balanced physique.
Nearly all compound lifts engage the core, improving posture and balance while reducing back pain risk.
By recruiting multiple muscles, compound exercises create a higher calorie burn per workout, making this program perfect for women looking to tone and lose body fat.
Resistance training supports better metabolism, bone health, and hormonal function—especially important for women over 30 or 40.
With only two workouts per week, this plan is realistic, flexible, and easy to maintain long term.
| Day | Workout | Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Monday | Workout A | Lower Body + Full Body |
| Tuesday | Rest or Light Cardio | Recovery |
| Wednesday | Rest | Recovery |
| Thursday | Workout B | Upper Body + Full Body |
| Friday | Rest | Recovery |
| Saturday | Optional Yoga/Cardio | Mobility |
| Sunday | Rest | Recovery |
This 2-day full body compound workout proves that less can be more when done correctly. Through smart programming and consistent effort, you’ll develop strength, tone, and endurance—without living in the gym.
Whether your goal is to build muscle, burn fat, or simply feel stronger in daily life, this plan fits perfectly into your lifestyle. Stay consistent, track your progress, and you’ll notice visible changes within weeks.
Stay up to date on the latest women’s health, fitness and lifestyle trends and tips.